This chapter explains each piece and component according to the flow.
Refer to tutorials(Realtime Message-DB tutorial) for handson guide.
Input/output data structures of interfaces are managed here. Data structure has 3 types.
Field is the smallest unit of a ISM data structure. Field is like a column of a table, an attribute of a C struct.
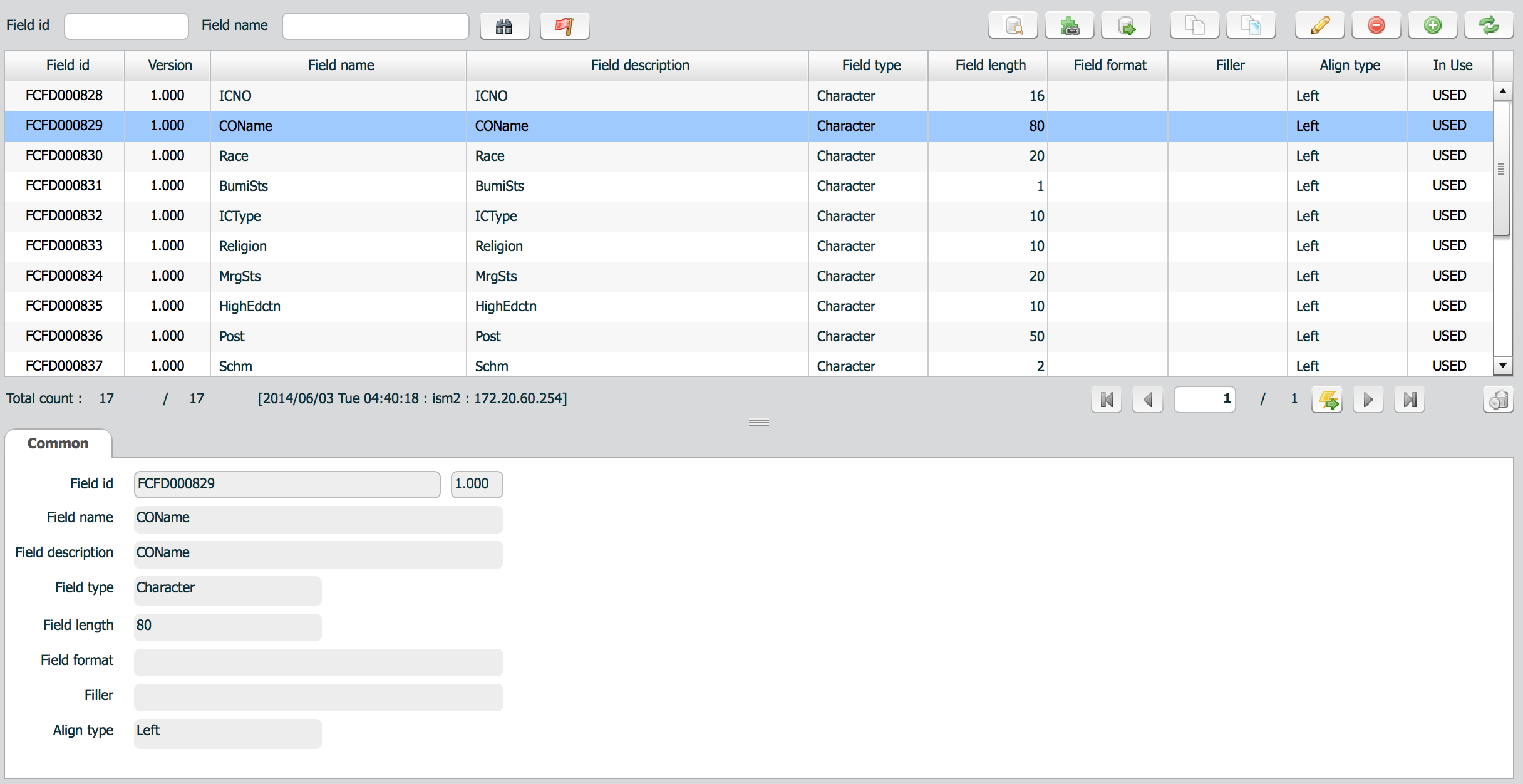
Field has some properties to be used for transformation, validation, and formatting.
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Field name | |
| Description | Field description | |
| Type | Field type | |
| Length | Field length | |
| Filler | Filler character when the length of a value is shorter than length | |
| Format | Field format. | Used to convert character to date type. |
| Alignment | Alignment of a field value. From left or right |
Field group is an ordered set of one or more fields. Field group is basic unit of ISM data structure.
Common tab defines general properties of a field group.
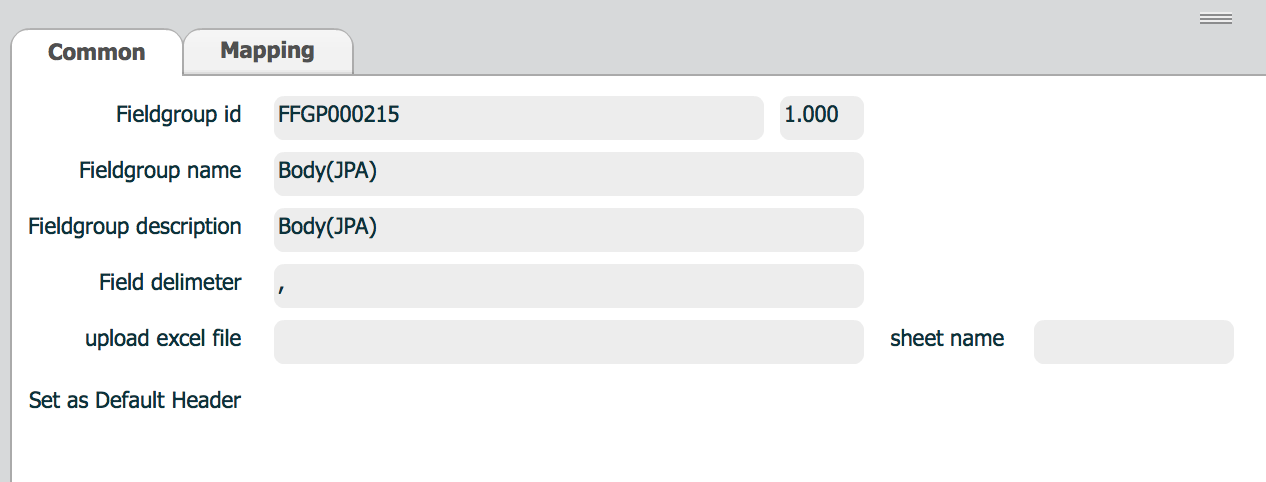
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Fieldgroup name | Field group name | |
| Fieldgroup description | Field group description | |
| Delimeter | Field group delimeter | Usually used for delimiter based file data |
| upload excel file | excel file name | |
| Sheet name | sheet name which contains field definition | Only used when field group is defined in an excel file. |
| Set as Default header | Check when this field group is used as commonly used header definition of a message | Used only for ISM data structure |
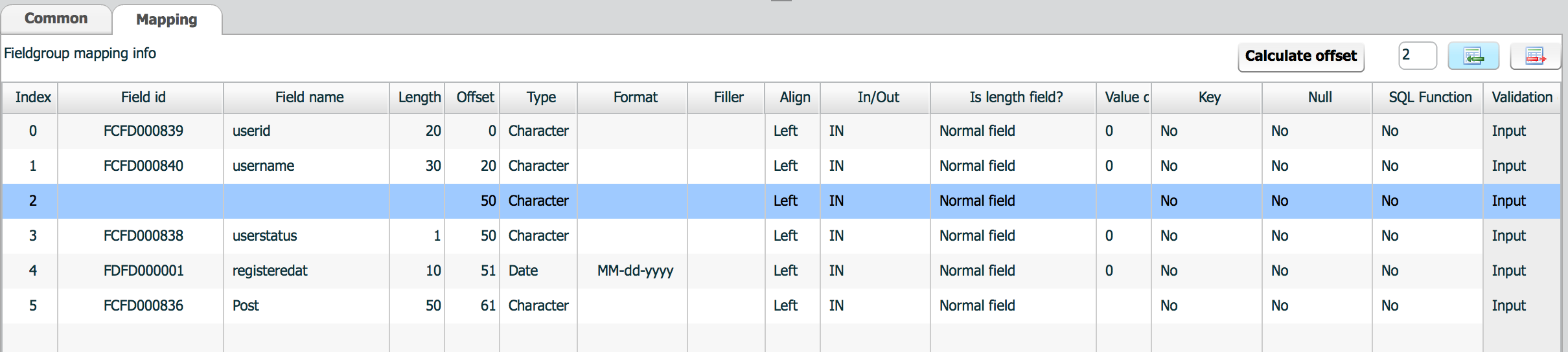
Mapping is to assign fields into a field group, to specify usage for each field in a field group.
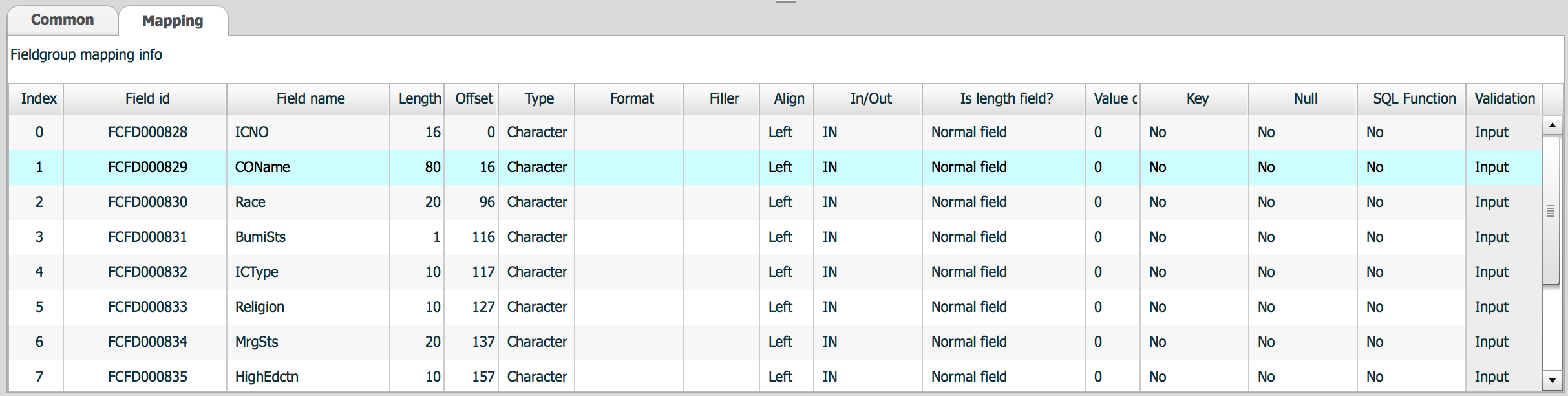
Properties of mapping table are followings.
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| index | Field index in this field group. Index starts from 0. |
| Field id | Field id from field definition |
| Field name | Field name from field definition |
| Length | Field length from field definition |
| Offset | Offset from index 0 in this field group |
| Type | Field type from field definition |
| Format | Field format from field definition |
| Filler | Filler from field definition |
| Align | Field align from field definition |
| In/Out | Field usage in this field group. Used for stored procedure. |
| Is Length field? | Field usage in this field group. Used for flat message. |
| Value diff | When this field is used as a length field, difference value to be minus. 8 means -8, -8 means add 8. |
| Key | Key field in this field group. Used for table operation. |
| Null | Nullable or not. |
| SQL Function | SQL Function or not. Used for query generation |
| Validation | Validation type |
Key is used for DB operation. One field group can have 0 or more key fields like a table. Key fields are used to generate condition parameters for
SQL Function is used during transformation. ISM generates query for target operation during transformation in batch/deferred interface. When ISM generates queries, it checks whether a field is used as a sql function. If the field is defined as a sql function, the result of transformation of that field is added to the generated query as a constant.
For example,
ISM will generate this query.
insert into target_table(col1, col2, col3) values(?, ?, ?);
if query is literal type, generated query will look like this.
insert into target_table(col1, col2, col3) values('col1_value', 'col2_value', 'SYSDATE');
ISM will generate this query.
insert into target_table(col1, col2, col3) values(?, ?, SYSDATE);
if query is literal type, generated query will look like this.
insert into target_table(col1, col2, col3) values('col1_value', 'col2_value', SYSDATE);
If input value of Nullable field is null, ISM will do
Go to mapping tab.
Click add field button(![]() ), a new row is appended at the end of the field list.
), a new row is appended at the end of the field list.
Click empty cell and popup field list dialog.
Select a field, and selected field is set to the new row.
To insert a field into a specific index, set index value and click add field button(![]() ).
).
To delete a field, select a field and click delete button(![]() )
)
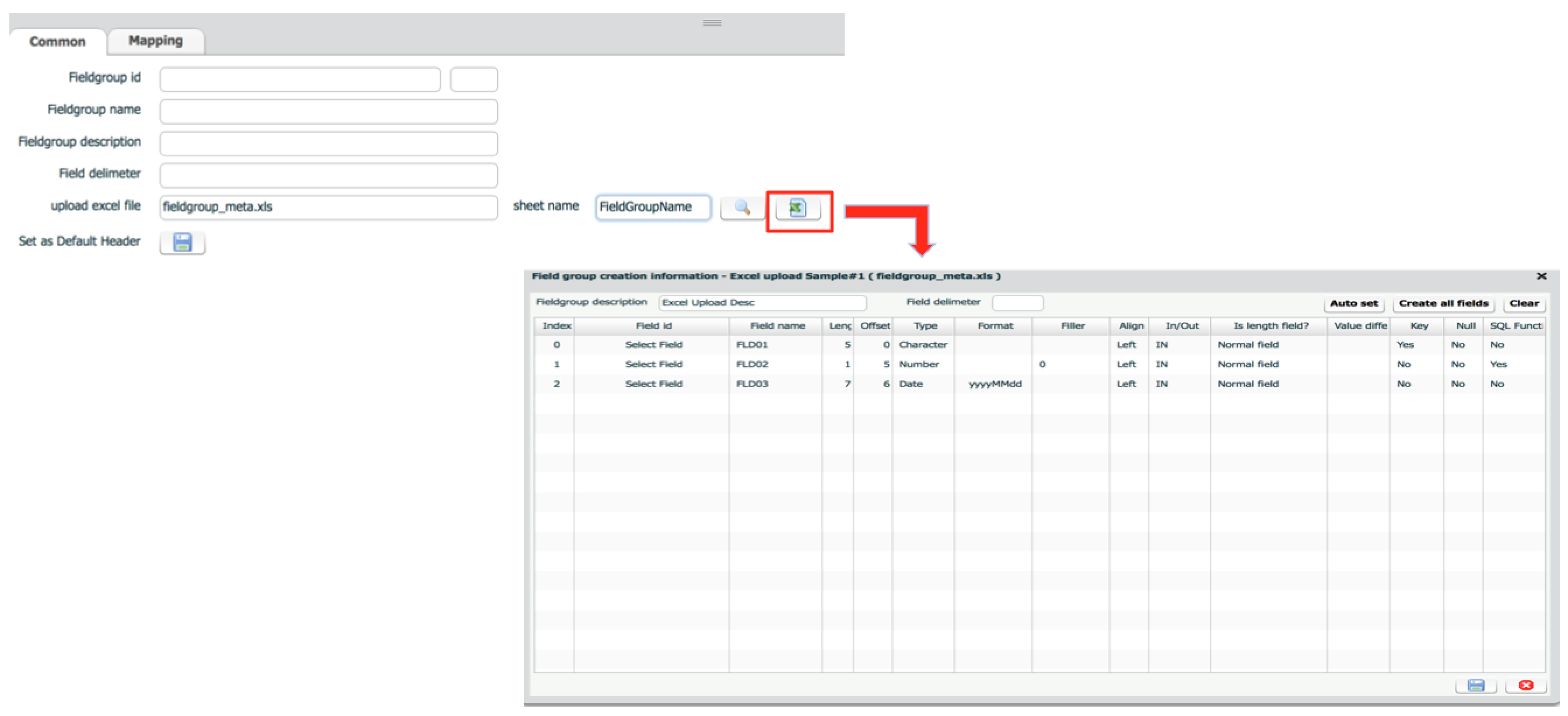
For the layout of excel file, refer to this file field group sample. This file is included under ISM_INSTALL_DIR/data.
ISM data structure defines
XML data is generated from sample xml.
ISM does not provide data structure generation from xml schema or DTD.
Refer to Message-DB Realtime tutorial for how to generate XML data structure.
System is a combination of application and server. One system can have one or more combinations of them. Usual production systems run same services on multiple servers.
Application defines type of software or package.
Common tab defines application type and account information(userid/password).
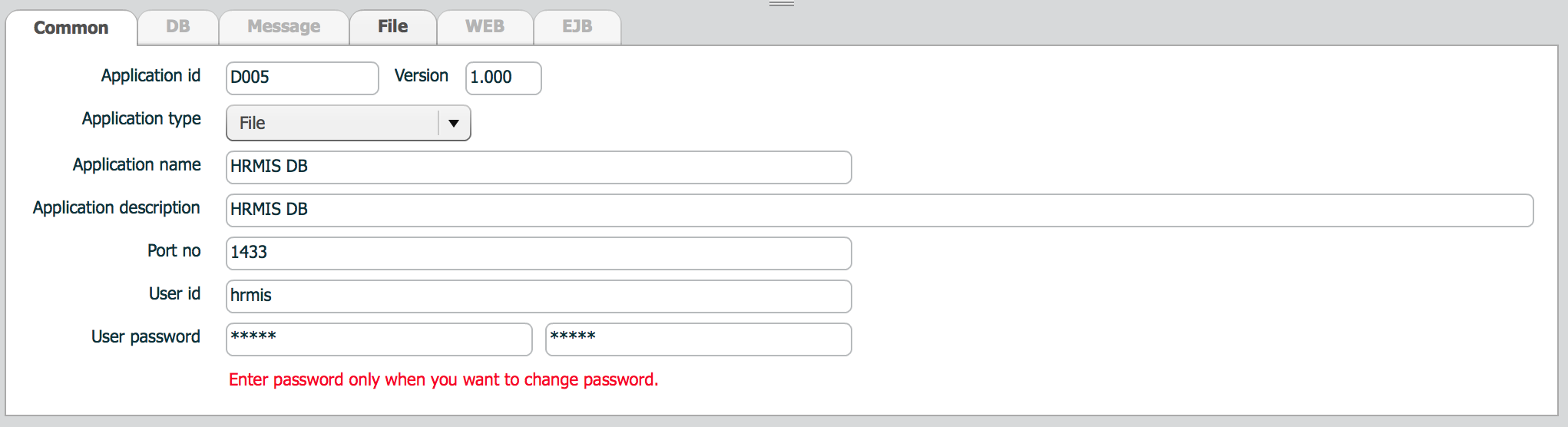
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Application type | Type of this application | |
| Application name | Name of this application | |
| Application description | Description of this application | |
| Port no | Listening port of this application | |
| User id | User id of this application | File, DB application requires user id |
| User password | Password | FIle, DB application requires user password |
ISM connects FTP or SSH daemon to get or put file(s).
ISM connects database servers via JDBC protocol. When DB application is used as a target and XA transaction is required, ISM uses platform provided adapter or datasource to communicate.
Defines Web server. ISM just calls http(s) url regardless the type of http application - php, asp, jsp, etc.
ISM communicates with J2EE servers via two protocols. One is JMS and the other is EJB. ISM uses Web application type to communicate other than JMS and EJB.
JMS type
EJB type
Message application is used to communicate with applications in which flat messages are used. Flat message usually have fixed length data.
These classification don't have different implementation. They just indicate what applications are running.
Etc type has no specific properties. It indicates that application is not in the application list.
Server defines physical host address or hostname.
System combines one application with one or more servers. ISM invokes service running on one of the servers against load balancing rule or constructs connection information like FTP or database.
Common tab defines general policies for that system. Load balancing and status management are defined.
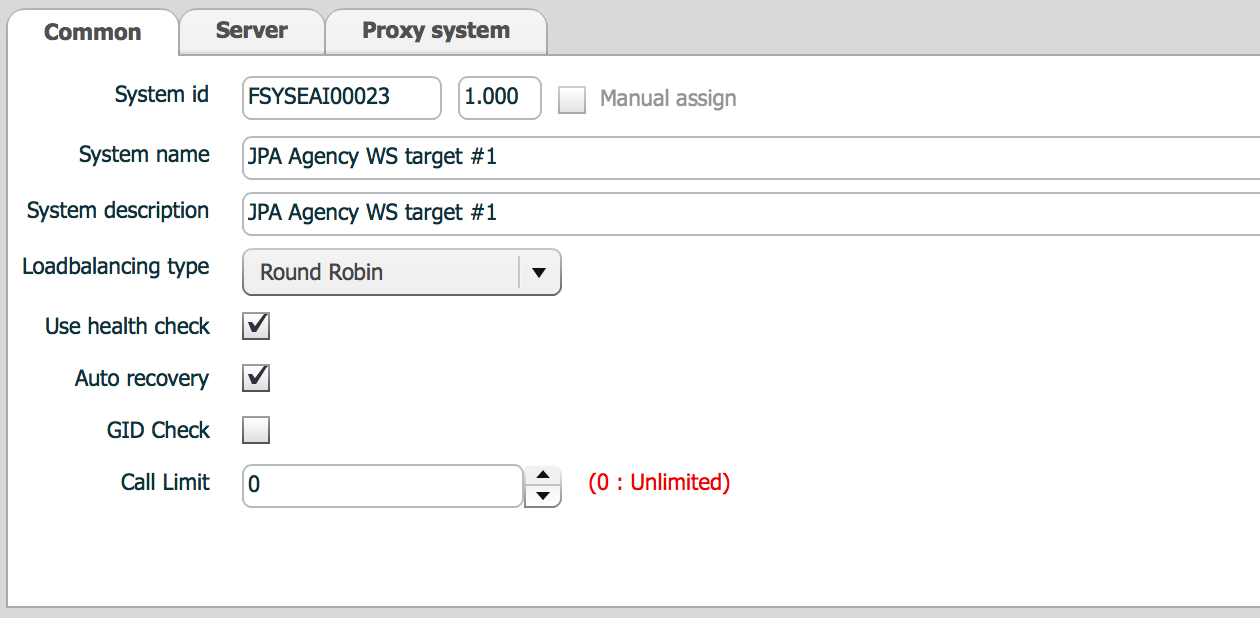
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| System name | System name | |
| System description | description | |
| Loadbalancing type | How to balance requests to servers in that system | Refer to Load balancing policy |
| Use health check | Determine health check is required or not | If check, when an error occurs, ISM tries to determine whether that error means system failure or not. Otherwise, ISM ignores system failure. Refer to Detect and recover of system failure. |
| Auto recovery | Determine change server status automatically | Used with Use health check property. |
| GID Check | Allow same transaction or not | GID is a identifying key of each transaction |
| Call limit | Determine how many requests can go to that system. | This property is ambiguous. Don't set other value than 0. |
Both Health check and auto recovery are on, then ISM tries to send dummy message for health check to that down server. The dummy message for health check is provided by user program. In ISM realtime ISM requires realtime parser. Realtime parser is used to extract information from input message and set value to outbound message. Another things parser should provide are ACK message and health check messages.
ACK message does not mean network level protocol but business level protocol. ACK is required, ISM ask parser to generate ACK message based on input message. ISM returns that ACK message to sender/source system.
Refer to Realtime parser for how to generate those messages.
Here ISM combines application and server and assign special properties to that combination related with load balancing policy.
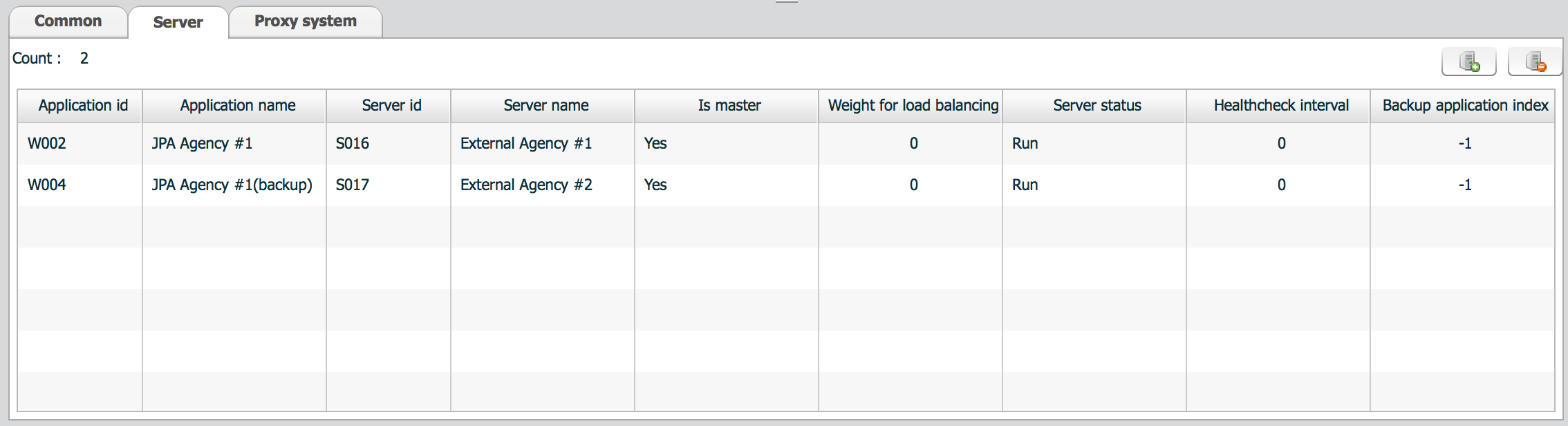
Click Add button(![]() ) to add a new combination.
) to add a new combination.
Click Application id or Application name cell to choose an application.
Click Server id or Server name cell to choose a server.
All the other properties of this combination are about load balancing policy.
This property is used when load balancing type is either
failover
dedicated
This property is used when load balancing type is
Default weight among the servers are same. Other value than 0 is assigned to a server, ISM sums up all the values and calculates weight per server.
Refer to Server status for values for available server status.
Default status value is No run.
To enable server status check, set status value to Run.
This value is used only when that server is down.
Interval means with which interval seconds ISM will try to check the status of that server.
This property indicates next server to invoke when this server is down. If the index is not assigned, i.e. -1, then ISM look for next master server from the list.
Proxy system is used in Businessware version.
System id of the proxy system is meaningful. Proxy system means what common process will be used to communicate to real target system for what type of interface. Refer to Types of proxy system for usage of proxy system
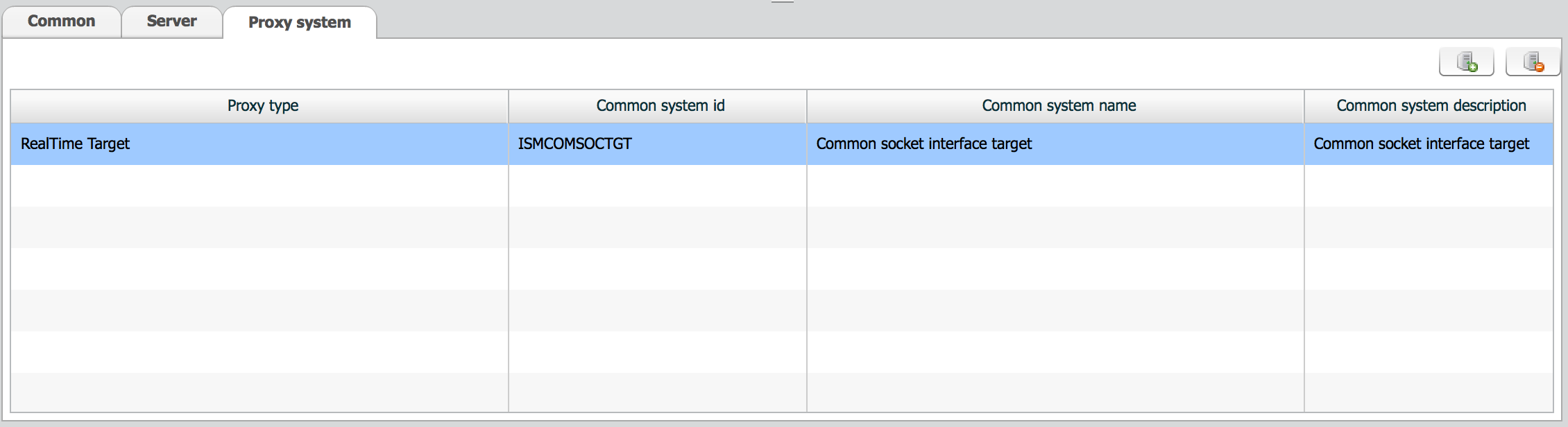
Common system is used for Businessware version only.
Common system stands for a process which is in charge of communication to multiple systems. Common system id is the only meaningful property.
Service is used to define what to do for source/target respectively.
For example, in a DB-DB batch interface, a service for source interface gets data from source system. Service definition for source interface contains query for getting data from source table. Service definition for target interface contains operation - CUD - and table name.
Common tab defines general policies for that system. Load balancing and status management are defined.

| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Service name | Service name | |
| Service description | description | |
| Input data structure | data structure used as input | |
| Output data structure | data structure used as output | |
| Error data structure | data structure used as error response | |
| Service type | service type | |
| Blocked | Service is blocked? | Used for realtime services to prevent bad service from affecting target system. |
DB Service tab defines table related operations.
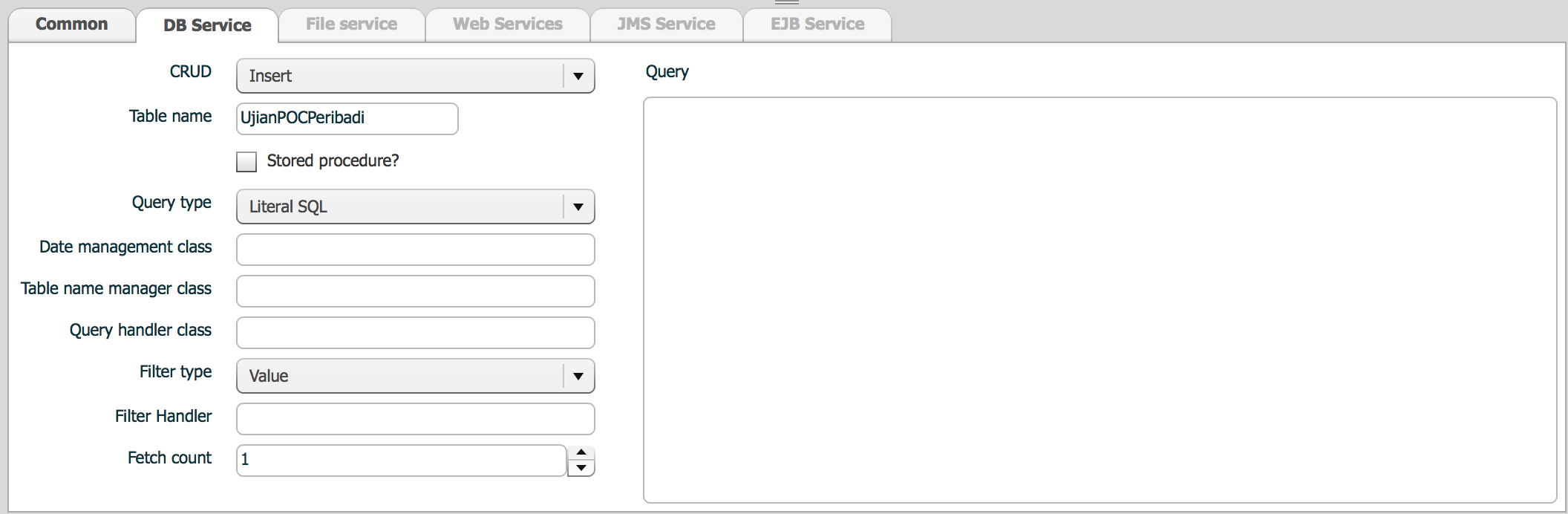
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| CRUD | DB operation | |
| Table name | Table name | |
| Stored procedure? | is target stored procedure? | Not used yet |
| Query type | JDBC query tyle |
|
| Date management class | date management class | |
| Table name manager class | Table name manager class | Used when table name contains #TABLE_NAME# parameter |
| Query handler class | Custom query generation class | Used when query generated by ISM cannot satisfy user requirements. Used for all the operation types. |
| Filter type | --- | |
| Filter handler | Used when Filter type is handler. | |
| Fetch count | --- | |
| Query | Used when CRUD value is one of select, user sql or user sql(skip error). |
This type is used only in realtime service for now.
ISM assumes query entered in the Query area as stored procedure call statement when Stored procedure property is checked. Query for stored procedure looks like this.
{call GetInterfaceWithOutput(#parameter_name#, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)}
ISM replace #parameter_name# with ? if query type is prepared. It means that prepared type query is used, ? can be used for input parameters.
Contents of stored procedure(mysql)
DELIMITER //
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS GetAllInterfaces;
CREATE PROCEDURE GetAllInterfaces()
BEGIN
SELECT 'GetAll', INTEGRATIONSERVICEID, ISTWOPHASECOMMIT, INTEGRATIONSERVICENAME, INTEGRATIONSERVICEDESC FROM integrationservice;
END //
DELIMITER ;
ISM query
{call GetAllInterfaces()}
Input data structure is not required.
Output data structure
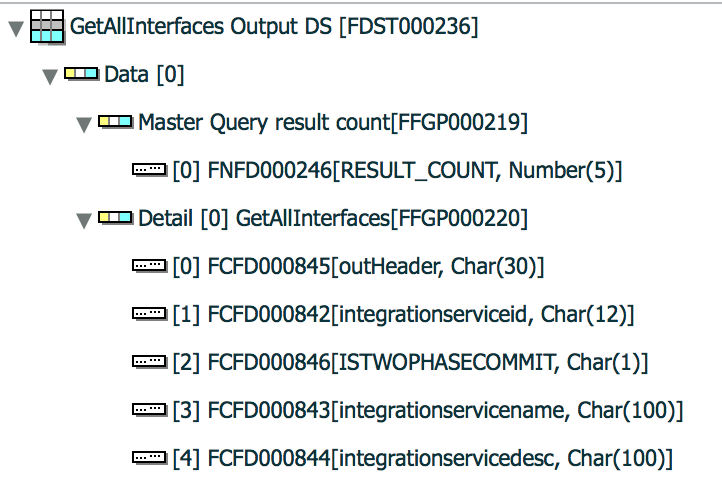
IN or OUT type value is not checked. Output data structure must contain one master field group with RESULT_COUNT field only.
RESULT_COUNT is fixed field name which indicates how many records exist in the return.
Contents of stored procedure(mysql)
DELIMITER //
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS GetFilteredInterfaces;
CREATE PROCEDURE GetFilteredInterfaces(IN id varchar(255))
BEGIN
SELECT 'GetFiltered', INTEGRATIONSERVICEID, ISTWOPHASECOMMIT, INTEGRATIONSERVICENAME, INTEGRATIONSERVICEDESC FROM integrationservice where integrationserviceid like concat ('%', id, '%');
END //
DELIMITER ;
ISM query
{call GetFilteredInterfaces(?)} or {call GetFilteredInterfaces(#id_filter#)}
Input data structure is used to for input parameter mapping.
Output data structure is same with the above case.
Contents of stored procedure(mysql)
DELIMITER //
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS GetInterfaceWithOutput;
CREATE PROCEDURE GetInterfaceWithOutput(IN id_filter varchar(255),
OUT out_header varchar(255),
OUT out_id varchar(255),
OUT out_2pc varchar(1),
OUT out_name varchar(255),
OUT out_desc varchar(255)
)
BEGIN
SELECT 'GetWithOutput', INTEGRATIONSERVICEID, ISTWOPHASECOMMIT, INTEGRATIONSERVICENAME, INTEGRATIONSERVICEDESC
INTO out_header, out_id, out_2pc, out_name, out_desc
FROM integrationservice where integrationserviceid like concat ('%', id_filter, '%');
END //
DELIMITER ;
ISM query
{call GetInterfaceWithOutput(#id_filter#, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)} or {call GetInterfaceWithOutput(?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)}
Input data structure
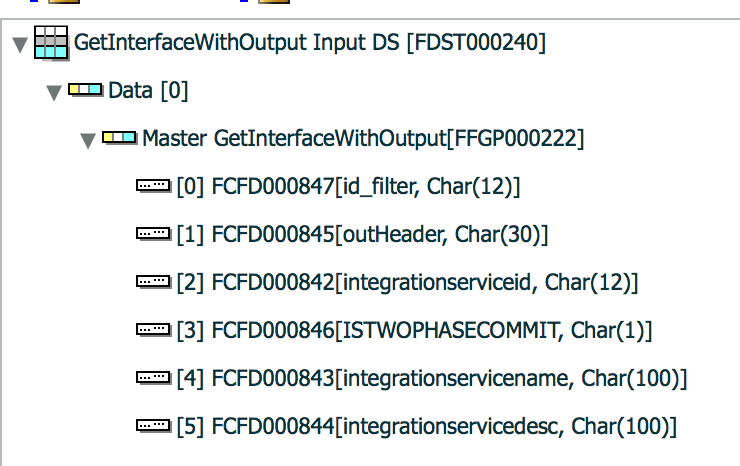
Input data structure must contain both input and output parameters to register output parameters while invoking stored procedure.
Output data structure

Input and output data structure must have same field group.
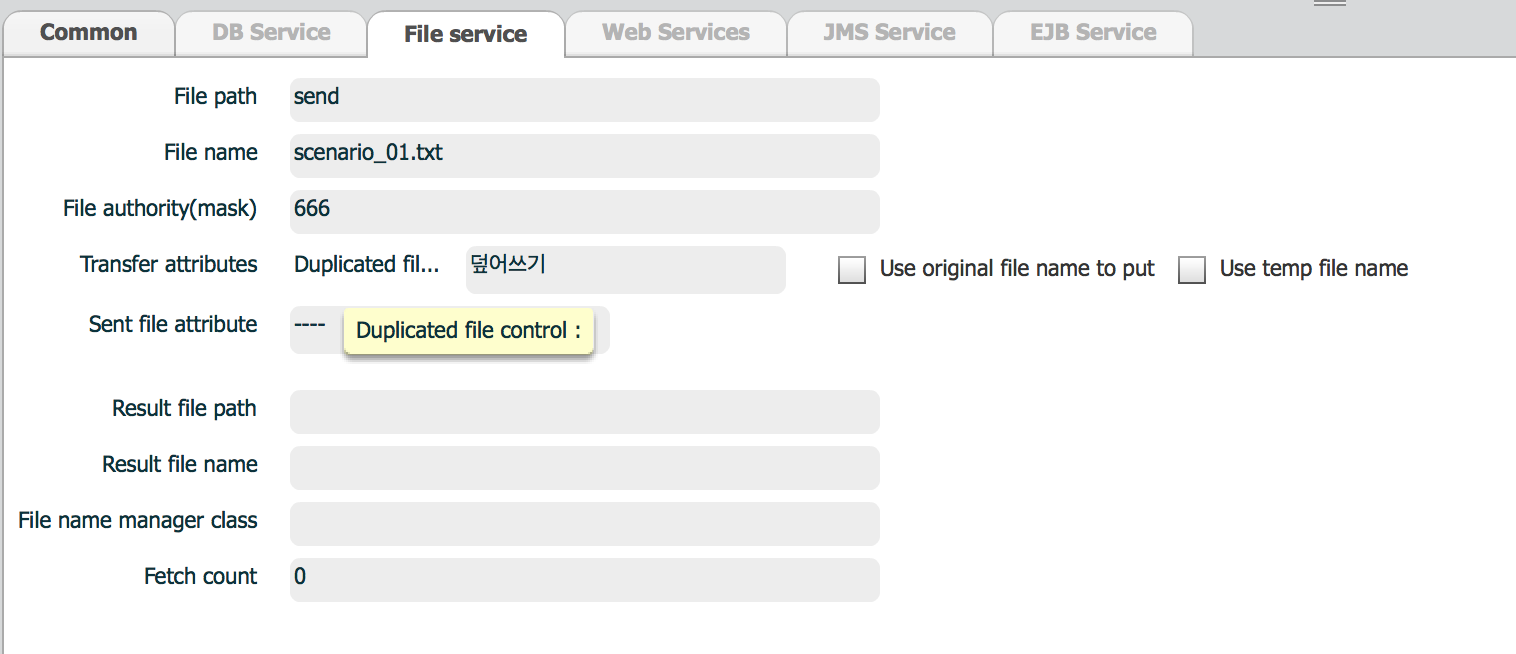
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| File path | directory for file(s) | |
| File name | file name | If file name is not specified here, ISM looks for a file name from input parameter |
| File authority(mask) | file mode | File mode - rwx, set as number |
| Transfer attributes | Duplicated file control |
Specifies what to do when a file with same name already exists,
|
| Use original file name to put | Use source file name | Used when this service is a target service. Use source file name, even if target file name is specified as a service property or input parameter. |
| Use temp file name | Use temporary file name to put file | Used when this service is a target service. ISM puts file data with temporary file name. After file transfer finished, ISM renames that temporary file to expected target file name. |
| Sent file attribute | Operation for source file after transfer |
|
| Result file path | Transfer result file path | Used to indicate file transfer is completed |
| Result file name | Transfer result file name | Used to indicate file transfer is completed |
| File name manager class | File name converter class | Used when file name contains parameters. Parameter is enclosed by #, for example #parameter_name#.
Refer to Custom handlers for implementation details. |
| Fetch count | --- | --- |
When a file service is used in realtime interface, it has return data with only one field named FILE_NAME.

FILE_NAME is fixed field name in ISM. The length can be modified.
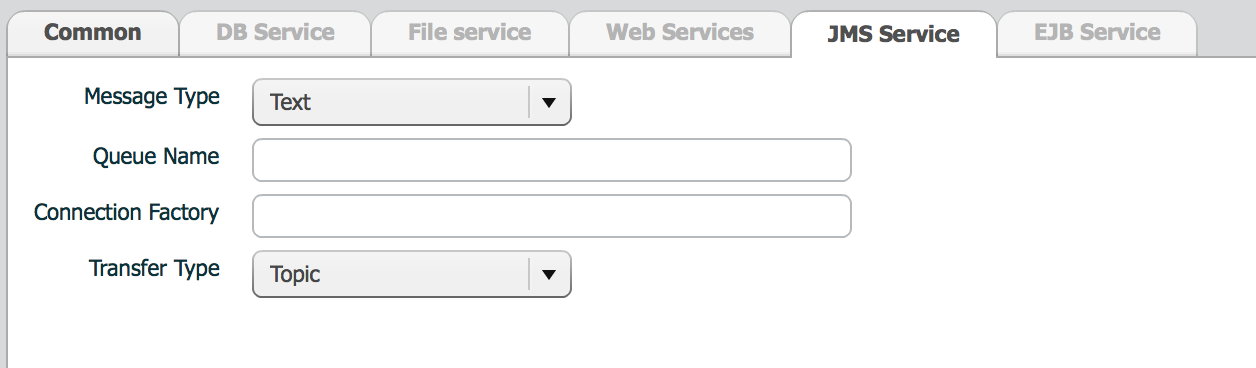
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| message type | JMS message type |
|
| Queue name | queue or topic name | |
| Connection Factory | JMS connection factory | --- |
| Transfer type | Queue or topic |
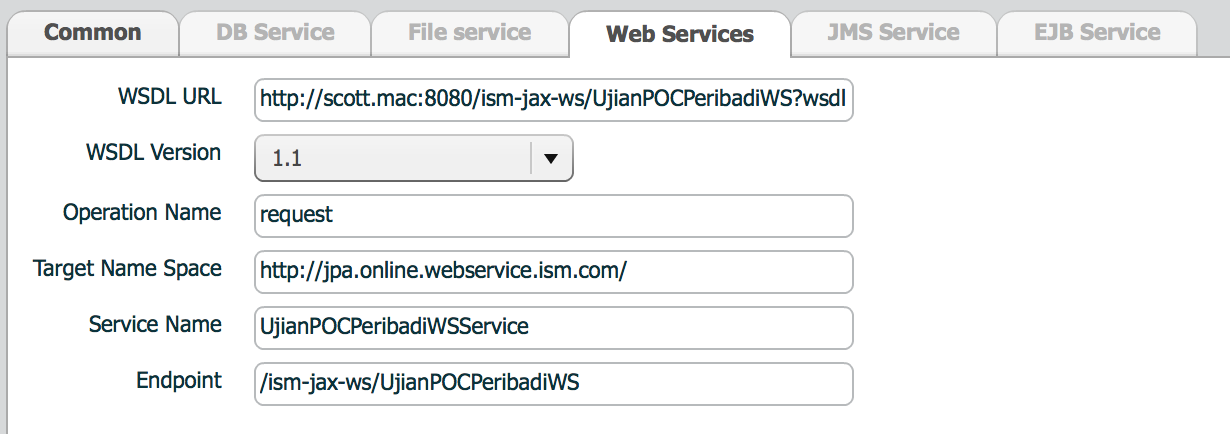
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| WSDL URL | WSDL url | |
| WSDL Version | WSDL specification version |
|
| Operation name | Operation to invoke |
Operation is defined as root element of Input xml data structure. Response of an operation is also defined as root element of output xml data structure. |
| Target Name Space | Web service name space | |
| Service name | Web service name | |
| Endpoint | URL for the web service | Endpoint does not include host:port |

| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| JNDI Name | JNDI name of EJB |
|
| EJB Version | EJB version |
|
Service mapping means every mapping involves output(s) of previous step(s) and input of next step. Each step stands for a service. One step may involve several output data to make its own input data.

Service mapping consists of one or more input services and one output service. Refer to File-DB Batch tutorial for the steps to define a mapping.
Data structures used for mapping are followings.
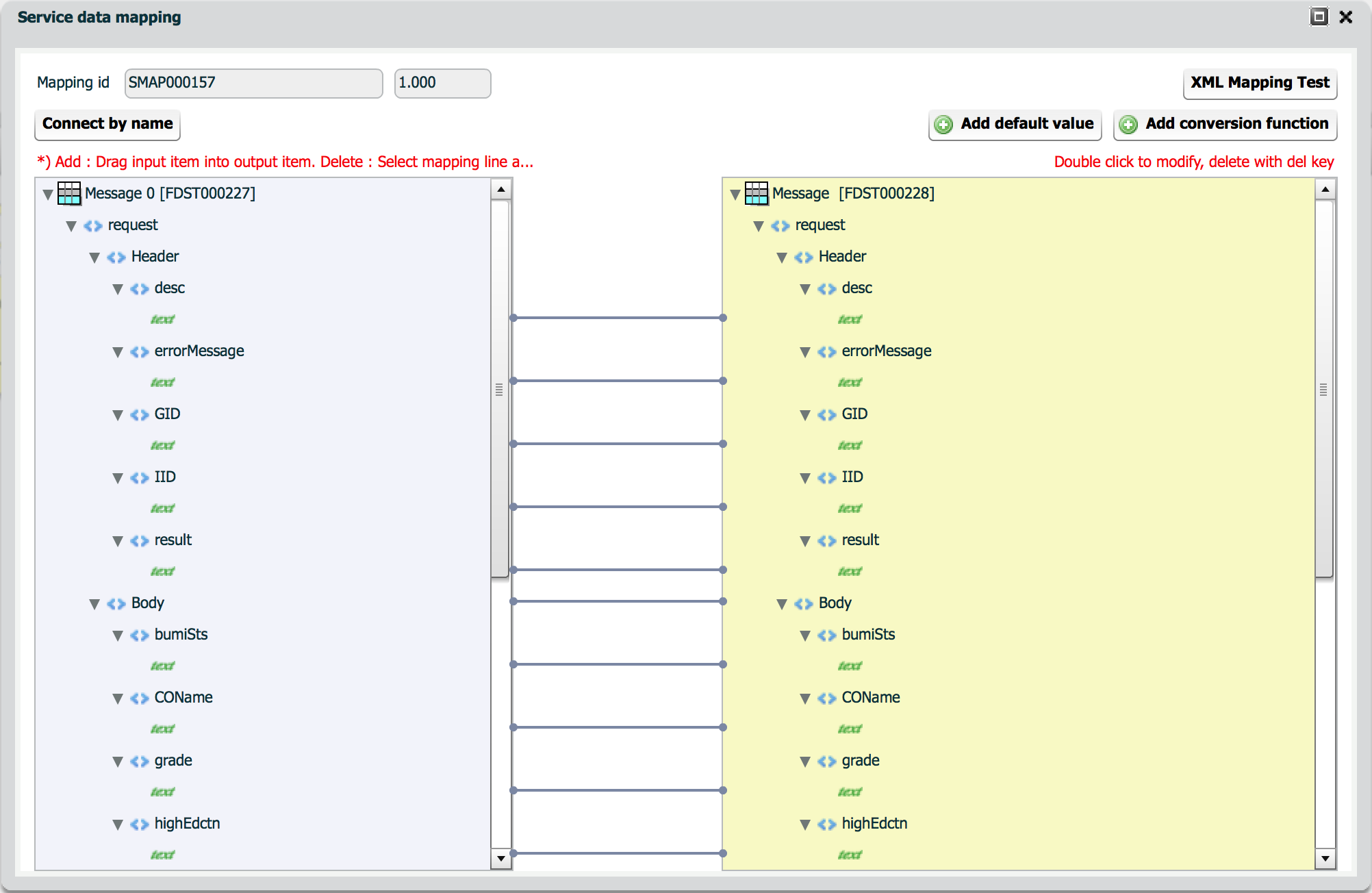
Function template manages user defined custom conversion functions.

User can create his/her own function in web console.

| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Function name | Function name | Function name is used as java class name. Naming convention follows java class naming convention. Special characters are not allowed. |
| Parameter count | parameter count | This property is used to generate function definition while mapping definition. |
| Function description | description of function | |
| Function code | Implementation code | Write user code here. |
If user code requires 3rd party libraries other than jdk like JDBC, write code in external IDE, and put compiled class to $ISM_HOME/custom directory.
Below is the bundled functions list.
| Function name | Description | Parameter count | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| CodeConverter | Code mapper. Used for simple code mapping. Ex) input value 'A' to 1, 'B' to 2 |
|
CodeConverter(CM00001, $1); |
| ltrim | Left trim. Remove left side space or newline of input value. |
|
ltrim($1); |
| rtrim | Right trim. Remove right side space or newline of input value. |
|
rtrim($1); |
| nvl | Return a certain value when input is null. |
|
nvl($1, a_value); |
| nvl2 | Return a certain value according to input for both null and not-null case. |
|
nvl2($1, null_value, notnull_value); |
| tolower | Convert input string value to lower case |
|
tolower($1); |
| toupper | Convert input string value to upper case |
|
toupper($1); |
Code mapping is used to convert meta code like values from one type to another type. It does not involve any calculation but map input value to output value.
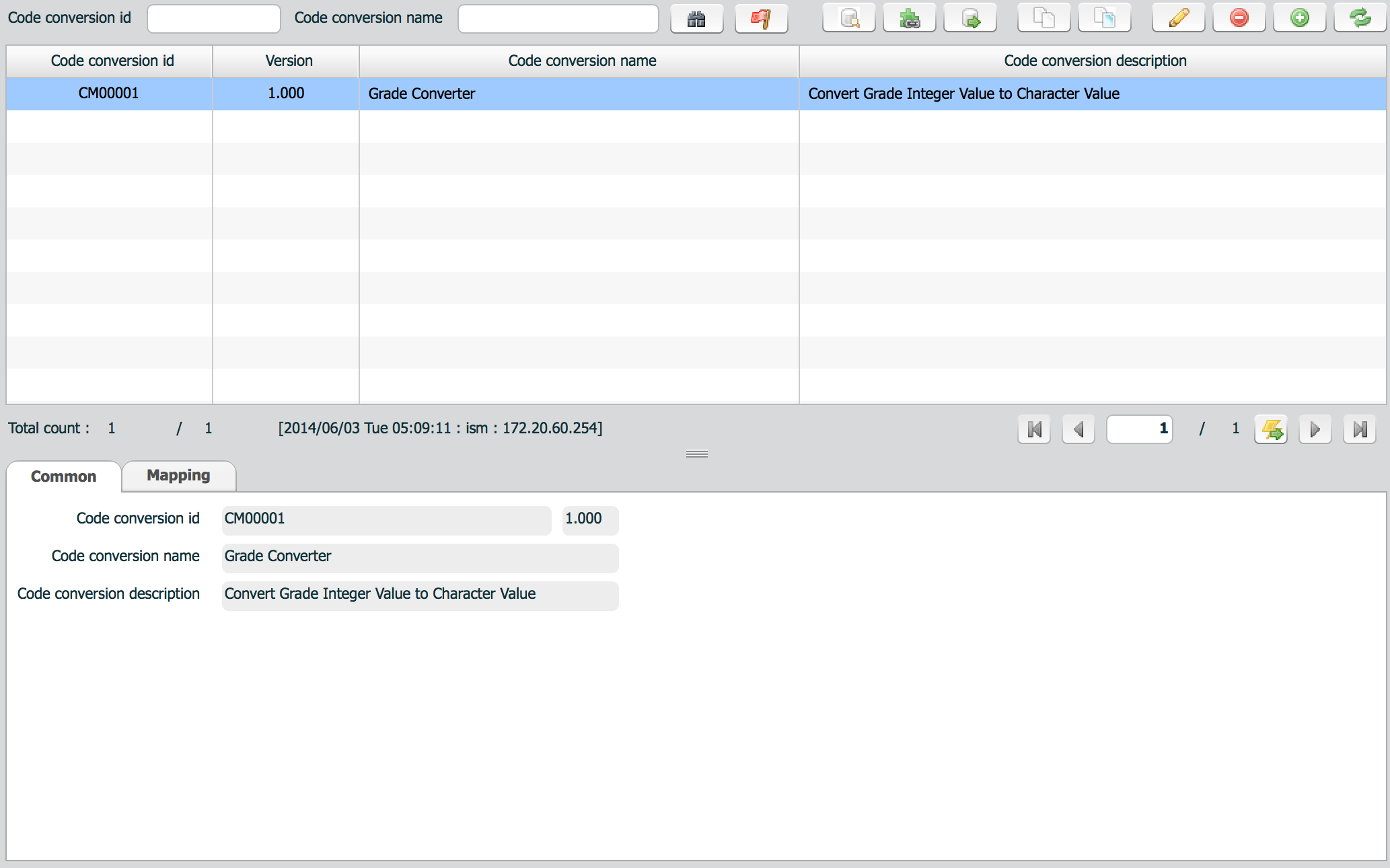
Common tab defines general explanation of code mapping definition.
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Code conversion id | code conversion id | Id is automatically generated. |
| Code converson name | code conversion name | |
| Code conversion description | description |
Mapping tab defines input/output value list.
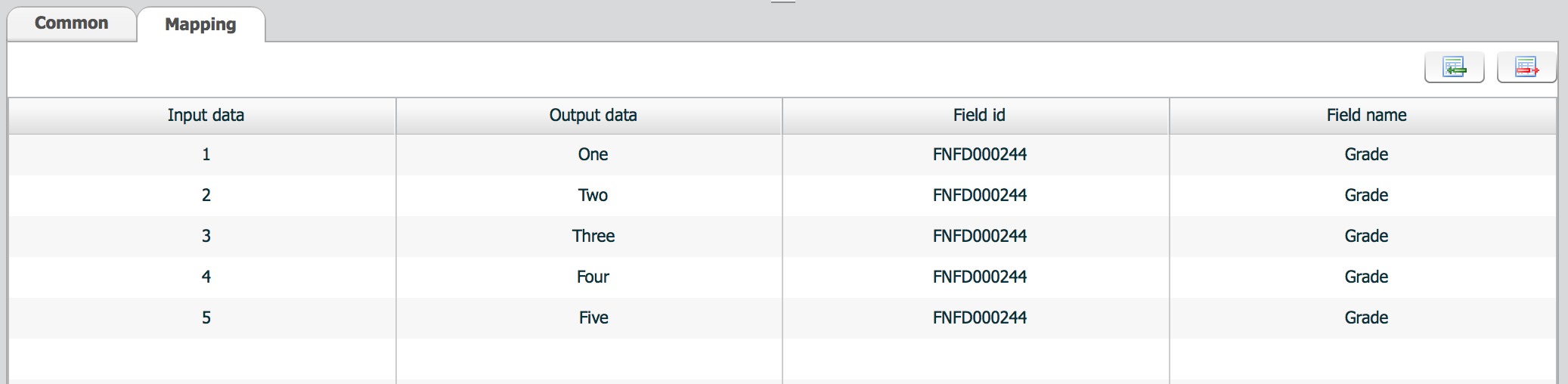
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| input data | input value | |
| output data | output value | |
| Field id | field id converted with this conversion | Field id is not used in conversion. It's just for information. |
| Field name | Field name from field id | Field name is also assigned for information. |
Service model defines flow of an interface. Physical system is not included in service model. User defines flow with previously defined service and mapping information. Refer to Realtime Message-DB tutorial.
Common tab defines basic information about a service model.
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Service model name | Name of service model | |
| Service model desc | Description of service model | |
| Concurrent processing | Parallel processing |
Used only in realtime and deferred services |
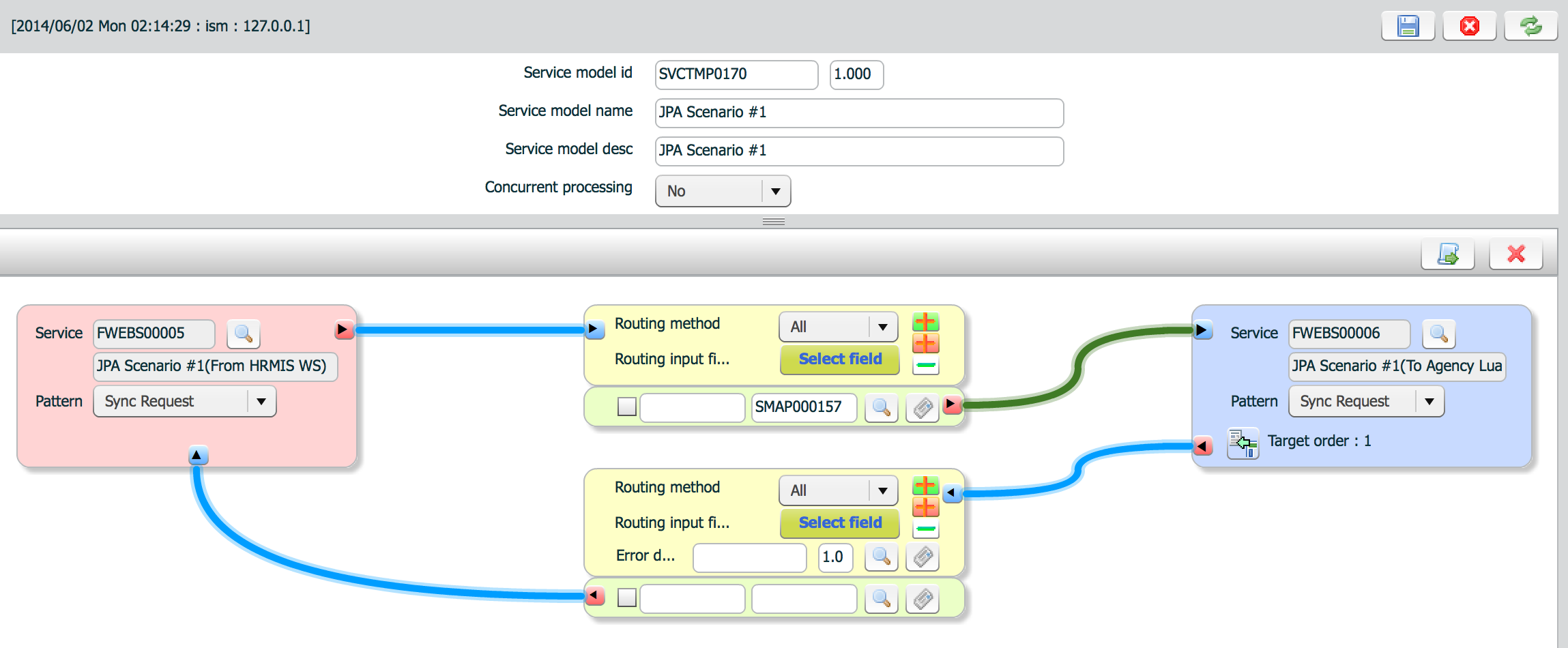
Flow design designs service flow from source to target(s) and how to.
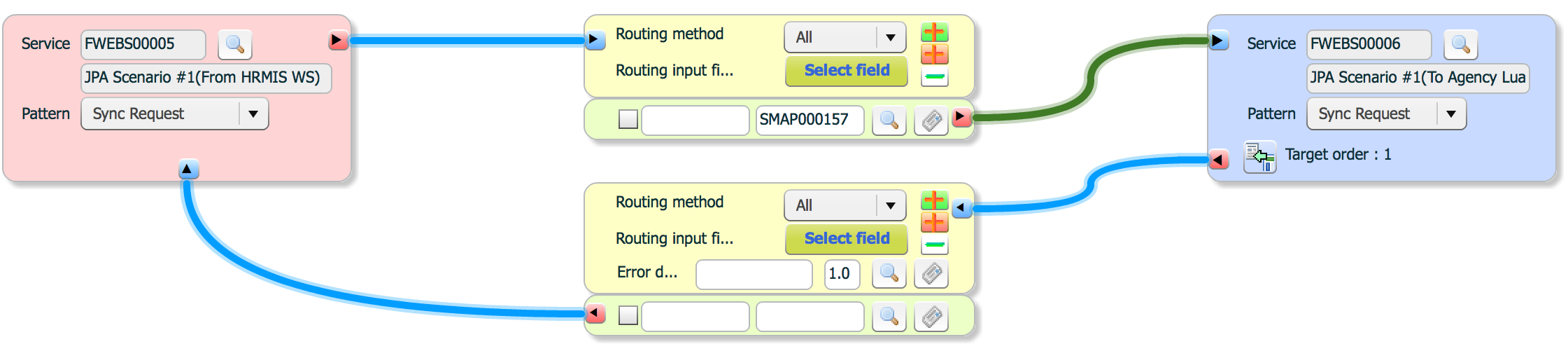
red button(![]() ) means send/request. blue button(
) means send/request. blue button(![]() ) means response.
) means response.
Routing has two types. One is used to send/request to target system. The other is used to respond to source or send/request to another target.
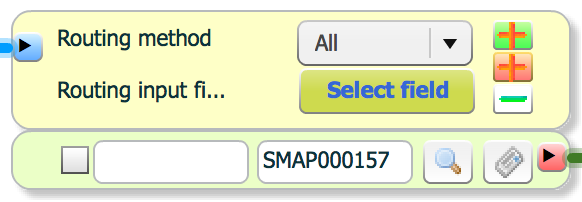

Routing method has four types.
To determine routing target, routing input field(s) are selected. Routing input(s) are selected from output messages of previous steps. Output messages are same with service mapping.

Pattern property is same with source.
Click routing button(![]() ) to add routing.
) to add routing.
Task is used to do pre or post processing before or after main processing in batch and deferred services. Each task consists a group of jobs.
One interface can have only one pre task and one post task at best.

Common tab defines basic information about a task.
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Task id | Task id | Id is generated automatically |
| Task name | Name of task | |
| Task description | Description of task |
Task tab defines a set of jobs. Each job is executed sequentially according to the index from 0. If a job fails, ISM stops processing.
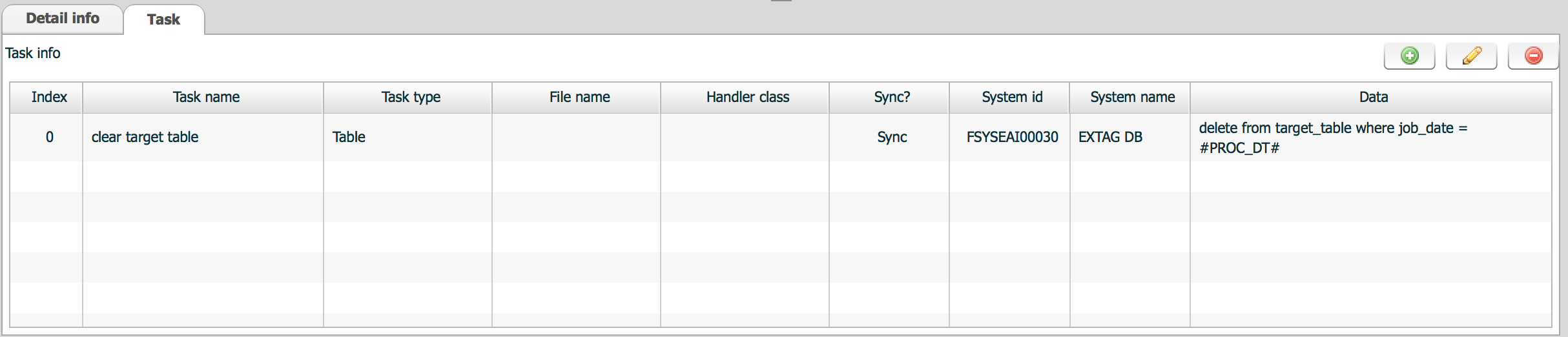
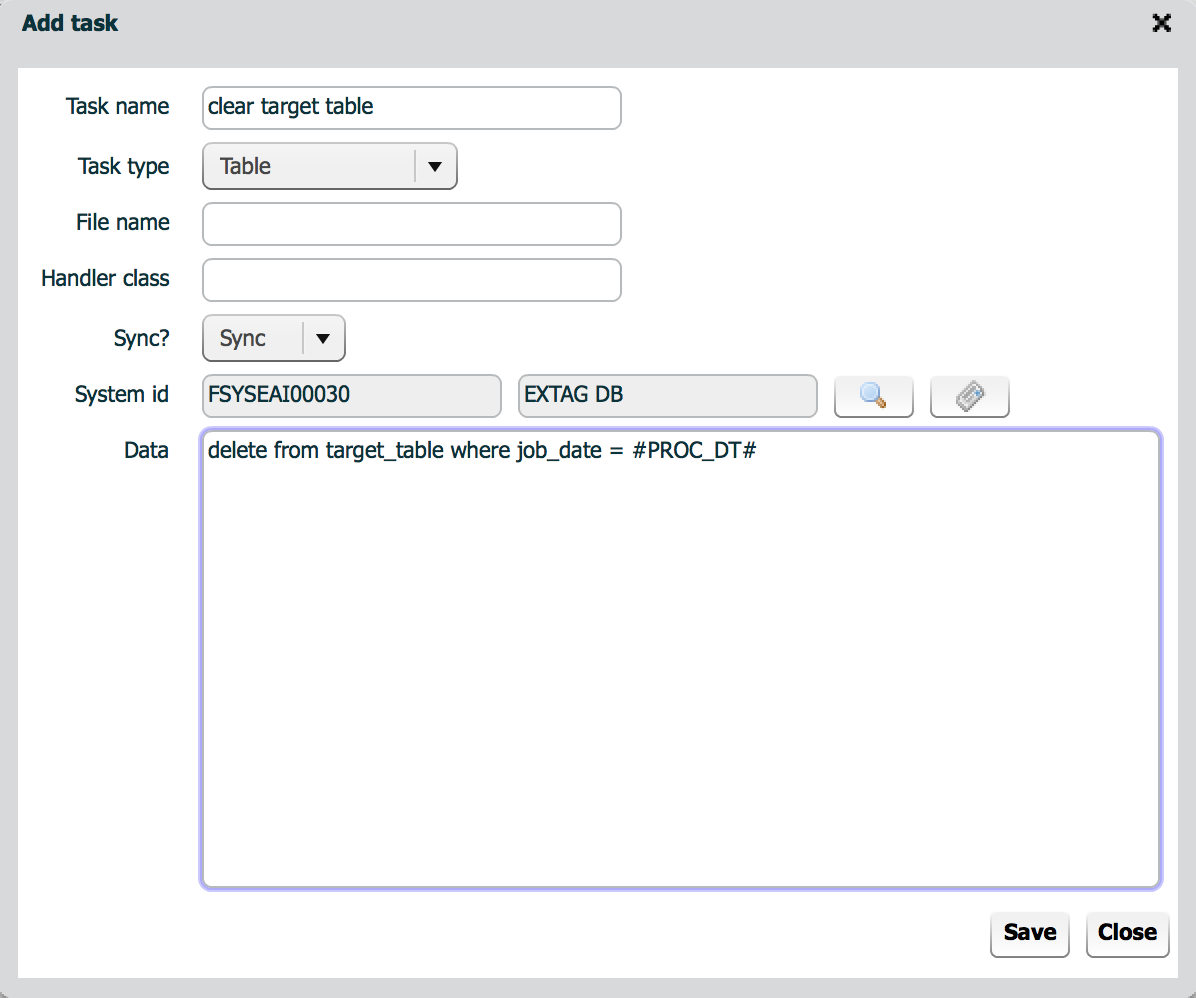
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Task name | Name of job | |
| Task type | Type of task | |
| File name | Name of file | Used in File task. |
| Handler class | Name of handler class | Used in Service and Custom task |
| Sync? | is sync? | Used in Service task. If async is selected, ISM does not wait response from job. |
| System id | System id to execute this job | System id is used to get connection information |
| Data | Data used as input for job |
|
Table task does not support select query. Even if you enter select query, ISM does not get query result. ISM just check whether the query is successful or not.
| attribute | description | usage | example |
|---|---|---|---|
| host name | Telnet host list, separated with comma(,) | #$telnet.host | ex) #$telnet.host=localhost |
| port | Telnet port, default port is 23. | #$telnet.port | ex)#$telnet.port=23 |
| user | telnet user id. multiple users are separated with comma(,) | #$telnet.user | ex)#$telnet.user=user1 |
| password | password Encrypted password must be assigned. When multiple users are assigned, separate with comma(,). |
#$telnet.password | ex)#$telnet.password=IUbOQ0vlgMKPF77kYaNmkw== |
| prompt | Telnet prompt After login, telnet server returns prompt. After prompt, user can execute command. The prompt format is different per server, so prompt format should be defined. When multiple servers should be defined like master and backup, each server is separated with comma(,). |
#$telnet.prompt | ex)#$telnet.prompt=/home/ism> |
| timeout | script execution timeout deafult is 60 seconds |
#$telnet.timeout | ex)#$telnet.timeout=120 |
| login prompt | After connection, telnet server returns login prompt. Login prompt is used to inform user to enter user id. The format of login prompt is usually ends with ogin:. No login prompt is assigned, default value used is ogin:. |
#$telnet.login.prompt | #$telnet.login.prompt=ogin: |
| password prompt | After user entered user id, telnet server returns password prompt. Password prompt is used to inform user to enter password. The format of login prompt is usually ends with assword:. No password prompt is assigned, default value used is password:. |
#telnet.password.prompt | #telnet.password.prompt=assword: |
(*) To encrypt password, use encrypt.sh(bat) command. $>encrypt.sh raw_string_to_be_encrypted
ex) /sw../../bin/util>encrypt.sh solulink IUbOQ0vlgMKPF77kYaNmkw==
ISM does not use output parameters after execution. ISM just checks whether execution is successful or not.
Stored procedure call query looks like this.
{call sp_name('string_param_value', number_param_value)}
Don't forget {} at both ends of the query.
Service task is used to invoke application or service on target system. This task generates message to be used to invoke ISM realtime interface and send to realtime module. That realtime interface forwards incoming message to target system and returns result to service task. Message handler class is used to generate message for ISM realtime interface. If no message handler class is defined, the value on data property is sent as it is.
To indicate function, enclose function invocation with <!, !>. If parameter(s) exist(s) inside function invocation, ISM converts parameters then invokes function. After function is executed, ISM pass the result to handler class.
<!F(#TGT_FILE_NAME#,20,1," ")!>
| F | Name of conversion function. java class name. |
| #TGT_FILE_NAME# | parameter name. User defined parameters can be assigned as pre or post parameters of batch agent. |
Refer to Service task function about how to implement a function.
Handler class is used for service task and custom task. Handler does
Refer to Task handler about how it is used and implemented.
Interface is final assembly of previously defined items.
are assigned here.
After generating interface, publish to master, validate(![]() ) whether it can be sent to runtime.
) whether it can be sent to runtime.
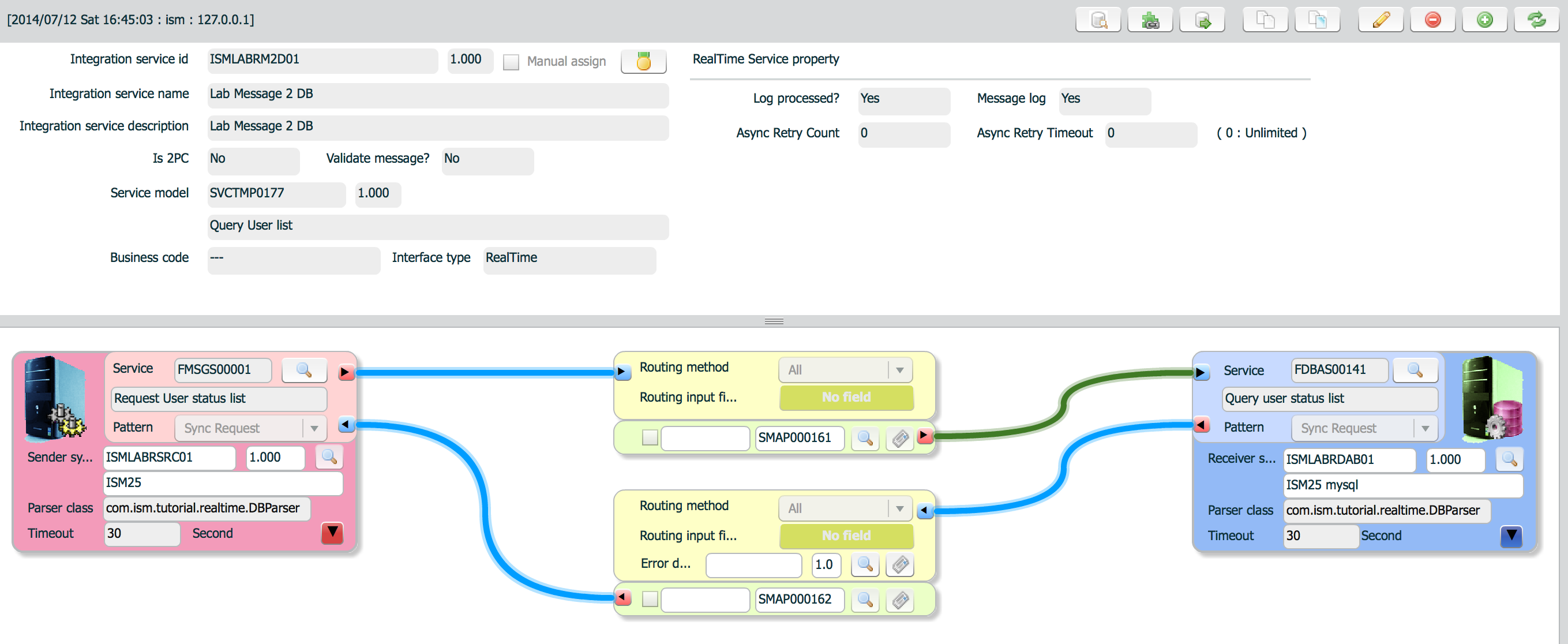
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| integration service id | Interface id | Key to identify an interface |
| integration service name | Name of interface | |
| integration service description | Description of interface | |
| Is 2PC | Flag to process as XA transaction or not | |
| Validate message? | flag to message validation | If validation is yes,
|
| Service model | Service model id | When creating a new interface, service model is selected first. |
| Business code | Business code of this interface | Not used |
| interface type | Interface type |
|

| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Log processed? | flag to log transaction result | Transaction results are stored in database |
| Message log | flag to log message | Messages are stored in file system |
| Async Retry Count | retry count | How many times to try to send a message to target systems when failed for asynchronous transfer? |
| Async Retry Timeout | retry time(seconds) | How long the failed message must not be maintained before purge for asynchronous transfer?
Example)
if retry timeout reaches after 4th retry, then ISM purges the message from the queue. If retry count reaches max before timeout reaches, then ISM purges the message from the queue. Default retry policy is unlimited retry until success. |
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| timeout | communication and service execution timeout included. |
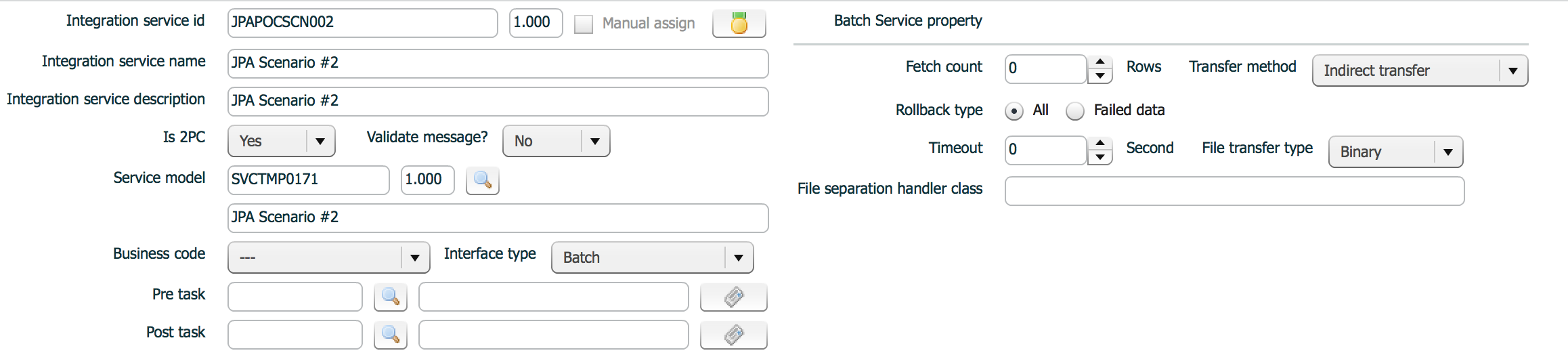
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Pre task | Jobs to be executed before main process | |
| Post task | Jobs to be executed after main process | |
| Fetch count | Processing uint. Record count in one processing |
If whole record count to be processed is greater than fetch count, ISM splits records per fetch count and process. Default fetch count is 10000, when 0 or nothing is assigned. |
| Transfer method | Transfer method |
|
| Rollback type | rollback type when a processing unit failed |
|
| Timeout | wait timeout of batch manager |
Data collection is performed in background.
Default Timeout is 60 seconds, , when 0 or nothing is assigned. |
| File transfer type | file mode |
|
| File separation handler class | File split class | Custom class when default split class does not fit the file structure.
Default file separation classses are
|
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| timeout | not used |
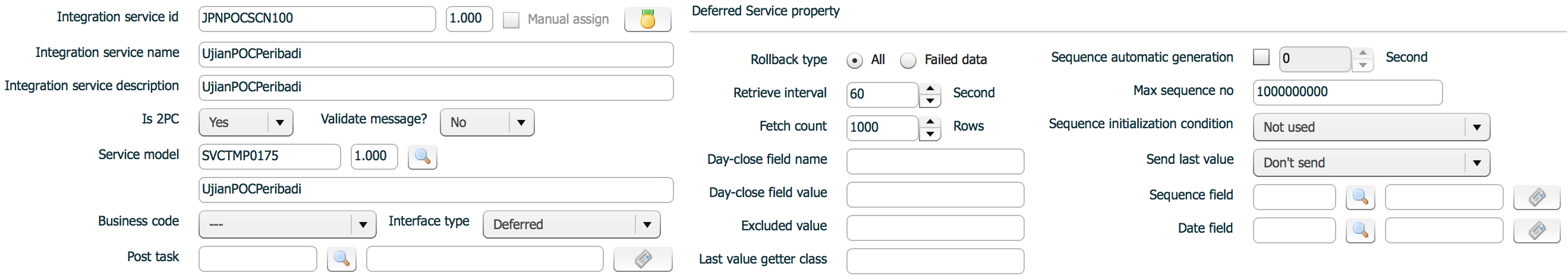
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Rollback type | rollback type when a processing unit failed |
|
| Fetch count | Processing uint. Record count in one processing |
If whole record count to be processed is greater than fetch count, ISM splits records per fetch count and process. Default fetch count is 10000, when 0 or nothing is assigned. |
| Retrieve interval | Timer interval(seconds) |
Default interval is 30 seconds, when 0 or nothing is assigned. |
| Day-close field name | Flag column to be used as an indicator of sequence initialization |
Used only when sequence initialization type is Change by day-close value |
| Day-close field value | Value of flag column to be used as an indicator of sequence initialization |
Used only when sequence initialization type is Change by day-close value |
| Excluded value | Not used | |
| Last value getter class | When next sequence to fetch is not managed in the source table or in different way. |
For example, sequence value is managed in a different table. |
| Sequence automatic generation | generation interval(seconds) |
When sequence value does not exist in source table and no other way to identify records to be processed, ISM recommends additional empty two columns which can be used as sequence and date field. ISM sequence generator fills up those two columns with sequence and current date and ISM will process based on the sequence. |
| Max sequence no | max sequence number |
If you want endless growth of sequence, set empty. |
| Sequence initialization condition | Sequence initialization type |
|
| Send last value | Flag to send day-close value to target or not | |
| Sequence field | Sequence field to be used for automatic sequence generation | |
| Date field | Date field to be used for automatic sequence generation |
| property | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| timeout | Not used |